Rhythmic Notation and Quantification
This page traces the works of the Music Representations team on rhythm and rhythmic quantification, from early works to the most recent developments of the OpenMusic computer-aided composition environment.
⇒ See also the IRCAM work group on rhythm and musical time
ANR-13-JS02-0004 EFFICACe
IRCAM UPI "Rhythm Quantification"
The RQ library
RQ is a new supervised approach to rhythm qiuantification, based on tree series enumeration. The library provides dedicated interface that allows to visualize and edit the transcriptions of the input sequence.
About rhythm quantification
Quantification is an well-known computer music problem. It consists in converting a stream of dates (typically expressed in seconds or milliseconds) into readable, traditional rhythmic notation.
Here are a number of external ressources describing it or proposing solutions.
- Peter Desain and Henkjan Honing, “The Quantization Problem: Traditional and Connectionist Approaches,” in Understanding Music with AI: Perspectives on Music Cognition, M. Balaban, K. Ebcioglu, and O. Laske, Eds. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1992.
- Ali Taylan Cemgil, Peter Desain, Bert Kappen, Rhythm Quantization for Transcription. Computer Music Journal, 24(2), 2000.
Previous works / Quantification tools in OM
Kant was the first quantification tool developed by the RepMus team in the early nineties.
- KANT : Une critique de la quantification pure. Carlos Agon Master's / DEA thesis (1994)
- Kant: a Critique of Pure Quantification. Carlos Agon, Gérard Assayag, Joshua Fineberg, Camilo Rueda. International Computer Music Conference (1994) [PDF].
- Problèmes de quantification et de transcription en composition assistée par ordinateur. Gérard Assayag, Peter Hanappe, Carlos Agon, Joshua Fineberg. Musique & mathématiques : Rencontres Musicales pluridisciplinaires GRAME (1996).
- Quantification et création musicale. Gérard Assayag, Gerorges Bloch, in Les modèles dans l'art, Musique, peinture, cinéma, sous la direction de M. Grabocz. Presses Universitaires de Strasbourg (1997).
OMKant is an OpenMusic library developed after Kant, proposing an user interface to control and supervise the Kant system. This library additional featured segmentation tools, tempo detection but did not survive to software environments evolution and is today no longer available.
- Organisation rythmique dans un environnement d’aide à la composition. Benoit Meudic, mémoire d'ingénieur IIE, Conservatoire National des Arts et Métioers (1999).
- Modélisation de structures rythmiques; Benoit Meudic, Masters / DEA Thesis, ATIAM (2000).
⇒ Hector Parra's contribution to The Om Composer's Book (volume 1) provides an example of application of OMKant (see parra.pdf pp.205-206)
Currently quantification processes are mostly carried out in OpenMusic visual programs throught the omquantify function.
- OMQuantify: OpenMusic quantification module in the OpenMusic user manual.
- Introduction to rhythm quantification: an older tutorial about quantification and omquantify in OpenMusic.
⇒ See Karim Haddad's chapters in The Om Composer's Books for examples of use of the omquantify tool: haddad-1.pdf haddad-2.pdf.
More recently the idea of segmenting and supervising the quantification process was brought forward again, thanks to a new architecture for score segmentation and analyse in OpenMusic, which can be used to perform piecewise segmentation of long musical sequences.
- New Framework for Score Segmentation and Analysis in OpenMusic. Jean Bresson, Carlos Pérez-Sancho, Sound and Music Computing Conference (2012).
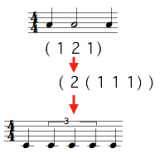
Rhythm Trees
Rhythmic processing and representations are based on the Rhythm Tree structures
- Représentation et rendu de structures rythmiques. Carlos Agon, Karim Haddad, Gérard Assayag. Actes des Journées d'Informatique Musicale - JIM (2002).
- Rhythm Trees in the OpenMusic user manual.
The idea of tree rewriting was explored in recent works to study the possible conversion of rhythm trees yielding equivalent notations.
- Pierre Donat-Bouillud presentation at the http://repmus.ircam.fr/rythme/\IRCAM work on rhythm (4/07/2013).
- Rhythm Tree Rewriting. Florent Jacquemard, Jean Bresson, Pierre Donat-Bouillud, Meeting of the IFIP WG 1.6 on Term Rewriting, Vienna Summer of Logic (2014).
- ⇒ Rewrite: a prototype OpenMusic library to manipulate and apply rewrite rules on rhythm trees, using a special syntax.
⇒ See A Structural Theory of Rhythm Notation based on Tree Representations and Term Rewriting. Florent Jacquemard, Pierre Donat-Bouillud, Jean Bresson, in Mathematics and Computation in Music: 5th International Conference, Springer Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence 9110 (2015). Extended version in A Term Rewriting Based Structural Theory of Rhythm Notation, Florent Jacquemard, Pierre Donat-Bouillud, Jean Bresson, Research Report ANR-13-JS02-0004-01 - EFFICACe (2015).